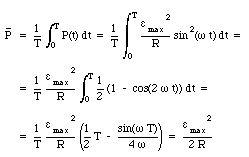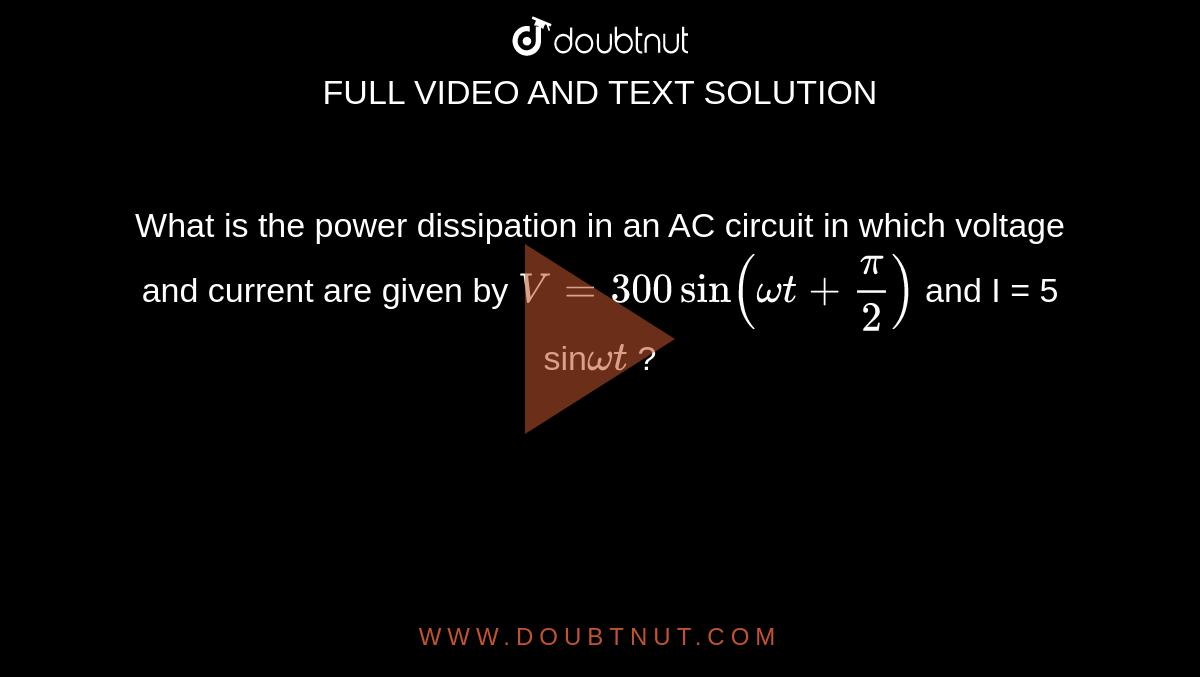
What is the power dissipation in an AC circuit in which voltage and current are given by V = 300 sin (omegat +(pi)/(2)) and I = 5 sin omegat ?

Voltage V and current i in AC circuit is given by V = 50sin(50 t) volti = 50sin (50t + pi/3 ) mA . The power dissipated in circuit is:
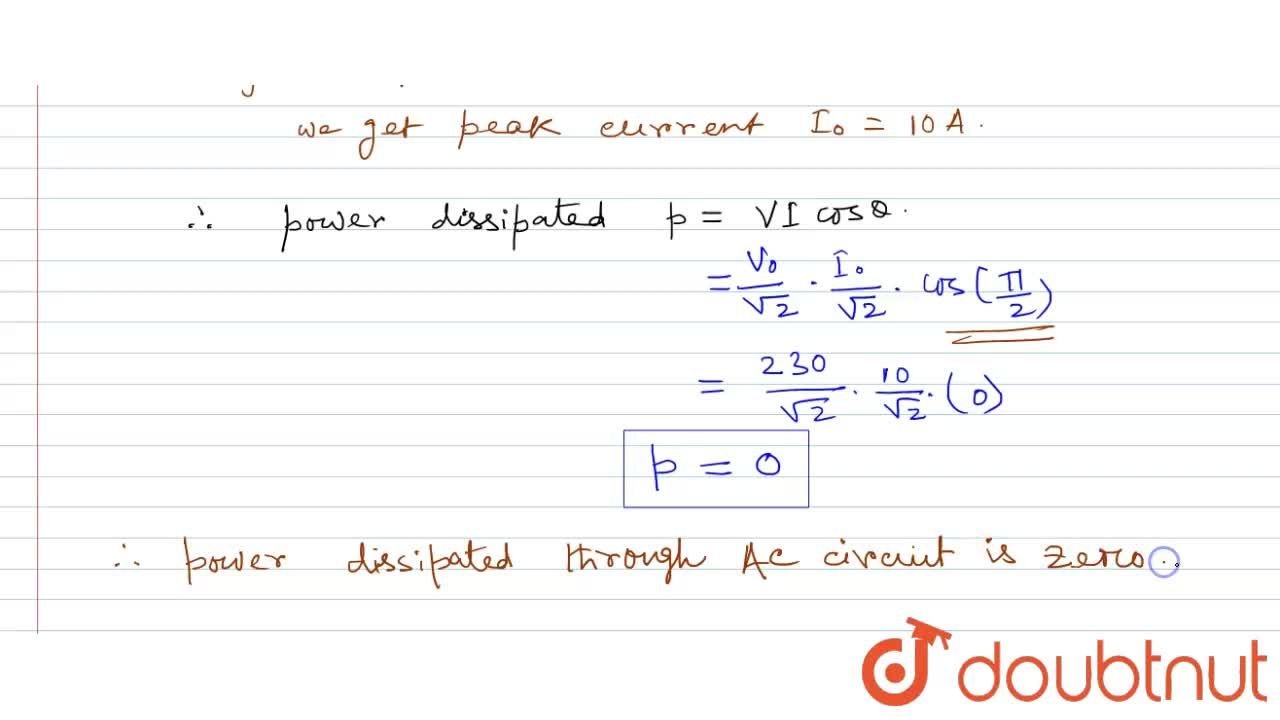
What is the power dissipated in an ac circuit in which voltage and current are given by V=230sin(omegat+pi/2) and I=10sinomegat?

Power dissipated in an `L-C-R` series circuit connected to an `AC` source of emf `epsilon` is - YouTube
Derive the expression for the average Power dissipated in a series LCR circuit for an ac source of a voltage, - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community
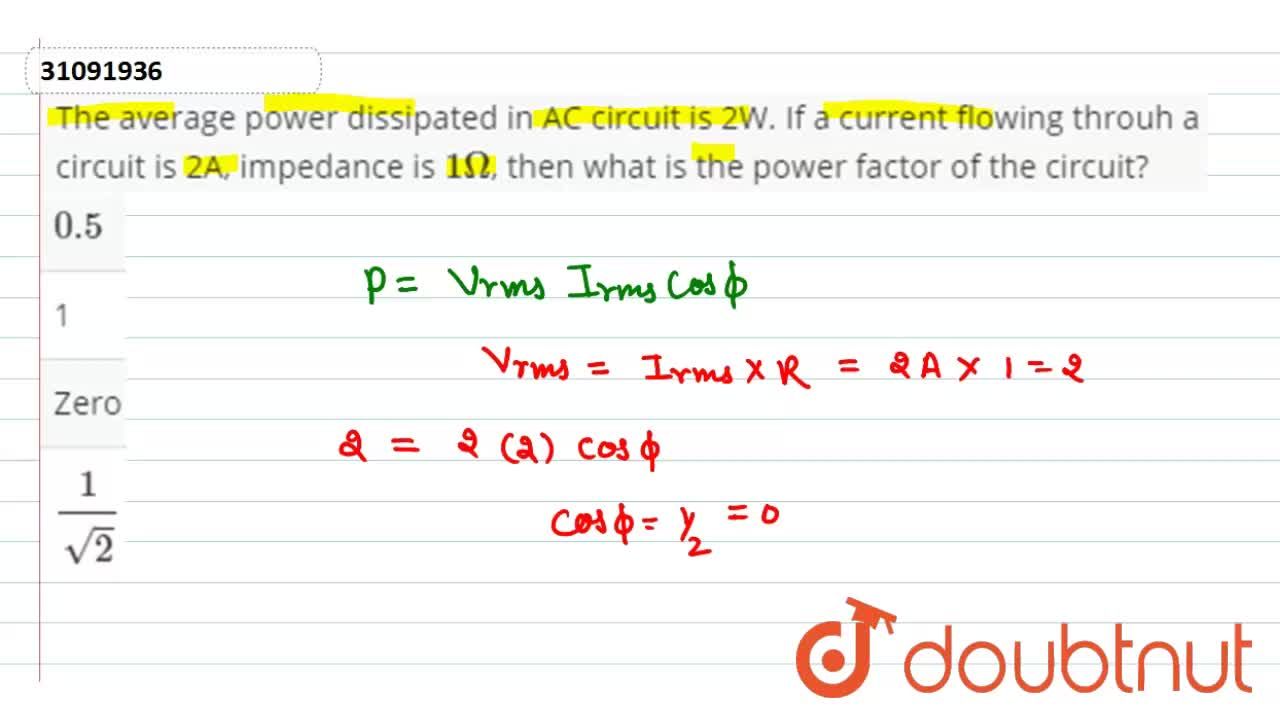
The average power dissipated in AC circuit is 2W. If a current flowing throuh a circuit is 2A, impedance is 1Omega, then what is the power factor of the circuit?
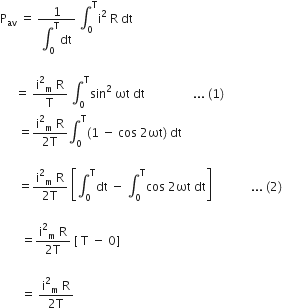
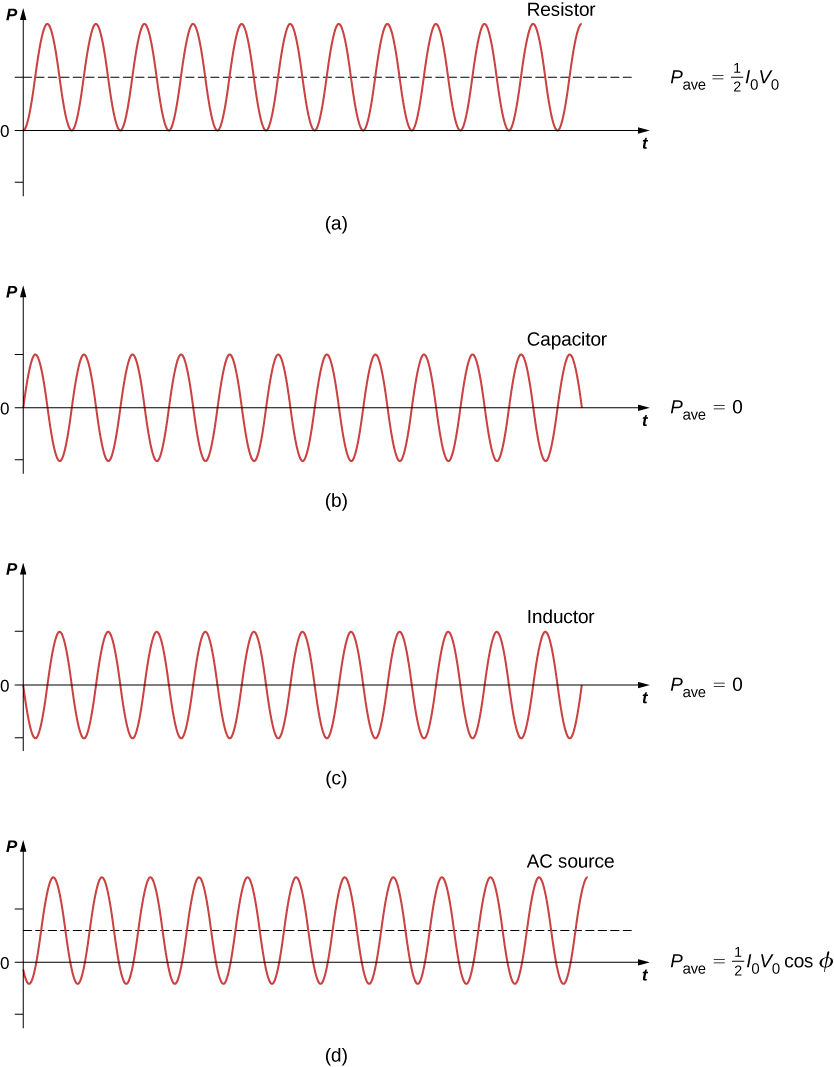
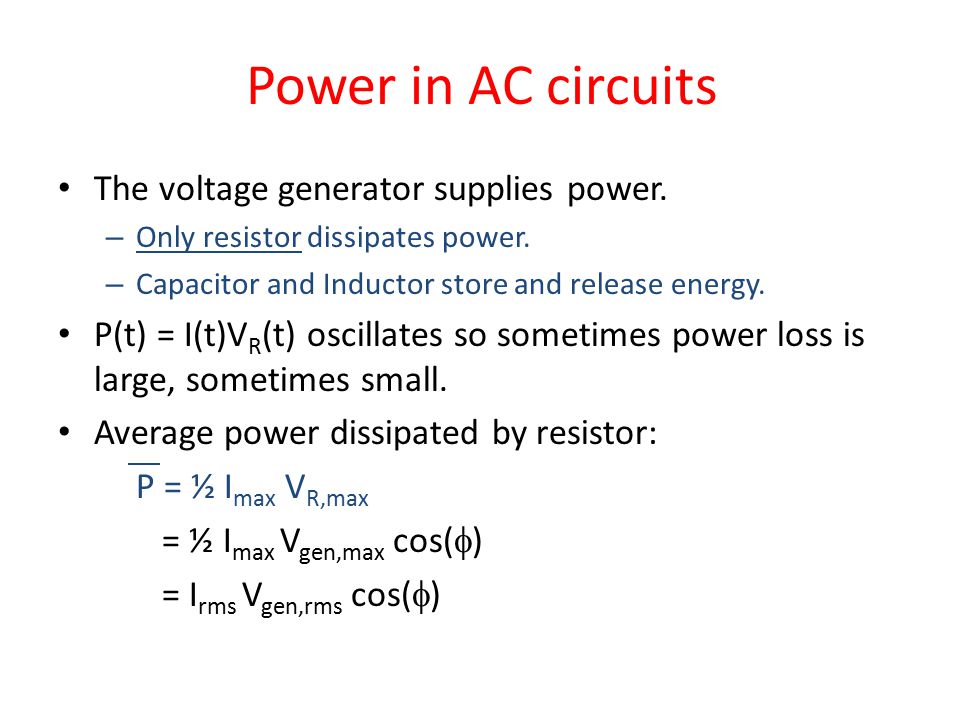
a) For a given a.c., show that the average power dissipated in a resistor R over a complete cycle is (b) A light bulb is rated at 100 W for a 220
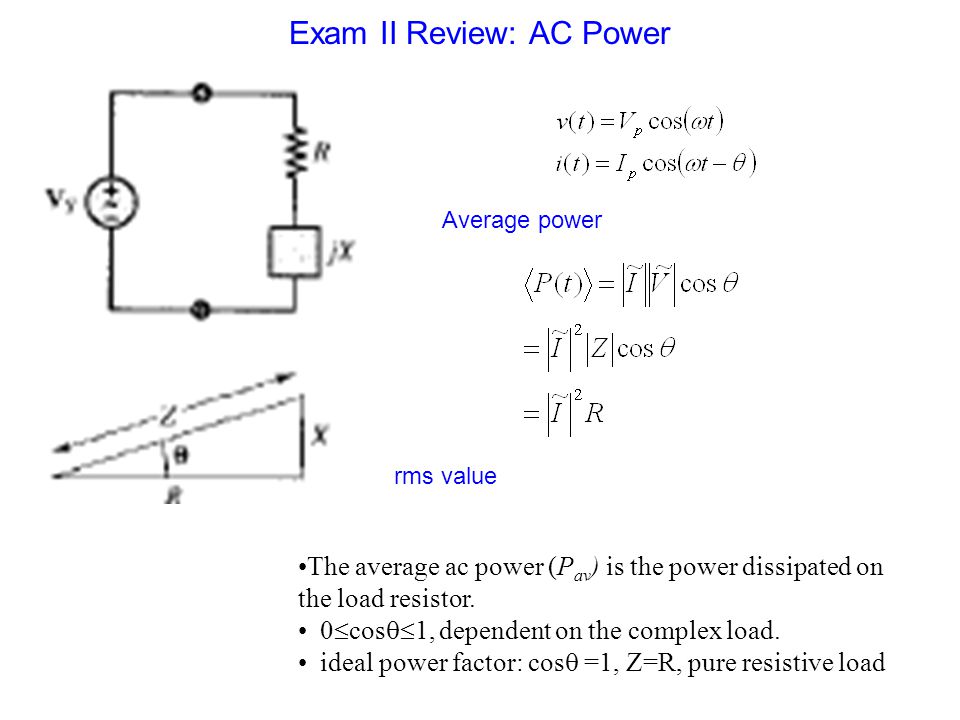
The average ac power (P av ) is the power dissipated on the load resistor. 0 cos 1, dependent on the complex load. ideal power factor: cos =1, - ppt download